Ammonium Nitrate Heat Of Formation
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ammonium nitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.680 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| United nations number | 0222 – with > 0.2% flammable substances 1942 – with ≤ 0.2% combustible substances 2067 – fertilizers 2426 – liquid |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| InChI
| |
| SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
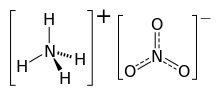
| Chemical formula | NH4NO3 |
| Tooth mass | eighty.043 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.725 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 169.6 °C (337.3 °F; 442.8 Thou) |
| Boiling point | approx. 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) decomposes |
| Solubility in h2o | Endothermic 118 k/100 ml (0 °C) 150 g/100 ml (20 °C) 297 grand/100 ml (40 °C) 410 g/100 ml (threescore °C) 576 g/100 ml (eighty °C) 1024 thousand/100 ml (100 °C)[one] |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -33.6·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Construction | |
| Crystal structure | trigonal |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | very low |
| Friction sensitivity | very low |
| Detonation velocity | 2500 m/s |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and wellness (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Explosive, Oxidizer |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |    |
| Indicate word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H201, H271, H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P220, P221, P264, P271, P280, P372 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1 0 three OX |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LDl (median dose) | 2085–5300 mg/kg (oral in rats, mice)[ii] |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Ammonium nitrite |
| Other cations | Sodium nitrate Potassium nitrate Hydroxylammonium nitrate |
| Related compounds | Ammonium perchlorate |
| Except where otherwise noted, information are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical chemical compound with the chemic formula NH4NO3 . It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in h2o and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agronomics as a high-nitrogen fertilizer.[four] Global production was estimated at 21.6 million tonnes in 2017.[five]
Its other major utilise is equally a component of explosive mixtures used in mining, quarrying, and civil construction. It is the major constituent of ANFO, a popular industrial explosive which accounts for 80% of explosives used in North America; similar formulations have been used in improvised explosive devices.
Many countries are phasing out its utilize in consumer applications due to concerns over its potential for misuse.[6] Accidental ammonium nitrate explosions have killed thousands of people since the early on 20th century.[6]
Occurrence [edit]
Ammonium nitrate is found as the natural mineral gwihabaite (formerly known as nitrammite)[seven] – the ammonium analogue of saltpetre (mineralogical name: niter)[8] [9] – in the driest regions of the Atacama Desert in Republic of chile, frequently as a crust on the footing or in conjunction with other nitrate, iodate, and halide minerals. Ammonium nitrate was mined there until the Haber–Bosch process fabricated information technology possible to synthesize nitrates from atmospheric nitrogen, thus rendering nitrate mining obsolete.
Production, reactions and crystalline phases [edit]
The industrial production of ammonium nitrate entails the acid-base of operations reaction of ammonia with nitric acrid:[10]
- HNO3 + NH3 → NHfourNO3
Ammonia is used in its anhydrous grade (a gas) and the nitric acid is concentrated. The reaction is violent owing to its highly exothermic nature. After the solution is formed, typically at about 83% concentration, the excess water is evaporated off to leave an ammonium nitrate (AN) content of 95% to 99.ix% concentration (AN melt), depending on class. The AN melt is then made into "prills" or small chaplet in a spray tower, or into granules by spraying and tumbling in a rotating drum. The prills or granules may exist further dried, cooled, then coated to prevent caking. These prills or granules are the typical AN products in commerce.
The ammonia required for this process is obtained by the Haber process from nitrogen and hydrogen. Ammonia produced past the Haber process can be oxidized to nitric acid by the Ostwald process. Some other product method is a variant of the nitrophosphate process:
- Ca(NO3)2 + 2 NH3 + CO2 + H2O → 2 NH4NO3 + CaCOthree
The products, calcium carbonate and ammonium nitrate, may be separately purified or sold combined as calcium ammonium nitrate.
Ammonium nitrate tin also exist fabricated via metathesis reactions:
- (NHfour)twoSO4 + Ba(NOiii)2 → 2 NH4NO3 + BaSO4
- NH4Cl + AgNOthree → NH4NOthree + AgCl
Reactions [edit]
As ammonium nitrate is a salt, both the cation, NH4 +, and the anion, NO3 −, may take part in chemical reactions.
Solid ammonium nitrate decomposes on heating. At temperatures beneath around 300 °C, the decomposition mainly produces nitrous oxide and water:
- NH4NO3 → Northward2O + 2H2O
At higher temperatures, the post-obit reaction predominates.[11]
- 2NH4NOthree → 2N2 + Otwo + 4H2O
Both decomposition reactions are exothermic and their products are gas. Under sure conditions, this tin can lead to a runaway reaction, with the decomposition process becoming explosive.[12] See § Disasters for details. Many ammonium nitrate disasters, with loss of lives, have occurred.
The ruddy–orange colour in an explosion cloud is due to nitrogen dioxide, a secondary reaction production.[12]
Crystalline phases [edit]
A number of crystalline phases of ammonium nitrate have been observed. The following occur under atmospheric pressure.
-
Phase Temperature (°C) Symmetry (liquid) (in a higher place 169.6) I 169.6 to 125.two cubic II 125.2 to 84.2 tetragonal III 84.2 to 32.three α-rhombic IV 32.3 to −16.8 β-rhombic V beneath −xvi.8 tetragonal[13]
The transition betwixt β-rhombic to α-rhombic forms (at 32.3°C) occurs at ambient temperature in many parts of the world. These forms have a three.six% deviation in density and hence transition betwixt them causes a change in volume. I applied issue of this is that ammonium nitrate cannot exist used equally a solid rocket motor propellant, as it develops cracks. Stabilized ammonium nitrate (PSAN) was developed every bit a solution to this and incorporates metallic halides stabilisers, which preclude density fluctuations.[14]
Applications [edit]
Fertilizer [edit]
Ammonium nitrate is an important fertilizer with NPK rating 34-0-0 (34% nitrogen).[xv] Information technology is less concentrated than urea (46-0-0), giving ammonium nitrate a slight transportation disadvantage. Ammonium nitrate's advantage over urea is that it is more stable and does not chop-chop lose nitrogen to the atmosphere.
Explosives [edit]
Ammonium nitrate readily forms explosive mixtures with varying properties when combined with explosives such as TNT or with fuels like aluminum powder or fuel oil. Examples of explosives containing ammonium nitrate include:
- Astrolite (ammonium nitrate and hydrazine rocket fuel)
- Amatol (ammonium nitrate and TNT)
- Ammonal (ammonium nitrate and aluminum powder)
- Amatex (ammonium nitrate, TNT and RDX)
- ANFO (ammonium nitrate and fuel oil)
- DBX (ammonium nitrate, RDX, TNT and aluminum powder)
- Tovex (ammonium nitrate and methylammonium nitrate)
- Minol (explosive) (ammonium nitrate, TNT and aluminum pulverisation)
- Goma-2 (ammonium nitrate, nitroglycol, Nitrocellulose, Dibutyl phthalate and fuel)
Mixture with fuel oil [edit]
ANFO is a mixture of 94% ammonium nitrate ("AN") and vi% fuel oil ("FO") widely used every bit a bulk industrial explosive.[16] : one It is used in coal mining, quarrying, metal mining, and civil construction in undemanding applications where the advantages of ANFO'southward low price, relative safety, and ease of use matter more than the benefits offered past conventional industrial explosives, such as water resistance, oxygen balance, high detonation velocity, and functioning in small diameters.[16] : ii
Terrorism [edit]
Ammonium nitrate-based explosives were used in the Sterling Hall bombing in Madison, Wisconsin, 1970, the Oklahoma City bombing in 1995, the 2011 Delhi bombings, the 2011 bombing in Oslo, and the 2013 Hyderabad blasts.
In November 2009, the government of the North West Frontier Province (NWFP) of Pakistan imposed a ban on ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, and calcium ammonium nitrate fertilizers in the former Malakand Division – comprising the Upper Dir, Lower Dir, Swat, Chitral, and Malakand districts of the NWFP – following reports that those chemicals were used past militants to make explosives. Due to these bans, "Potassium chlorate – the stuff that makes condom matches catch fire – has surpassed fertilizer every bit the explosive of pick for insurgents."[17]
Niche uses [edit]
Ammonium nitrate is used in some instant cold packs, as its dissolution in water is highly endothermic. In 2021, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi arabia conducted experiments to study the potential for dissolving ammonium nitrate in water for off-grid cooling systems and equally a refrigerant. They suggested that the water could be distilled and reused using solar energy to avoid water wastage in severe environments.[18]
Information technology was once used, in combination with independently explosive "fuels" such as guanidine nitrate,[nineteen] [twenty] as a cheaper (merely less stable) alternative to five-aminotetrazole in the inflators of airbags manufactured by Takata Corporation, which were recalled as dangerous later killing xiv people.[21]
Prophylactic, handling, and storage [edit]
Numerous safety guidelines are bachelor for storing and handling ammonium nitrate. Health and rubber information are shown on the prophylactic data sheets available from suppliers and from various governments.[22] [23] [24]
Pure ammonium nitrate does non fire, but as a strong oxidizer, it supports and accelerates the combustion of organic (and some inorganic) material.[22] [25] [26] It should non exist stored near combustible substances.
While ammonium nitrate is stable at ambient temperature and pressure under many conditions, it may detonate from a strong initiation charge. It should not be stored near high explosives or blasting agents.
Molten ammonium nitrate is very sensitive to shock and detonation, especially if it becomes contaminated with incompatible materials such as combustibles, flammable liquids, acids, chlorates, chlorides, sulfur, metals, charcoal and sawdust.[27] [22]
Contact with sure substances such as chlorates, mineral acids and metallic sulfides, can lead to vigorous or fifty-fifty violent decomposition capable of igniting nearby flammable cloth or detonating.[28] [29]
Ammonium nitrate begins decomposition after melting, releasing NO x , HNOiii, NH
iii and H2O. It should not be heated in a confined space.[22] The resulting estrus and pressure from decomposition increases the sensitivity to detonation and increases the speed of decomposition. Detonation may occur at eighty atmospheres. Contamination can reduce this to twenty atmospheres.[27]
Ammonium nitrate has a disquisitional relative humidity of 59.4% at xxx°C. At higher humidity it volition blot moisture from the atmosphere. Therefore, it is important to store ammonium nitrate in a tightly sealed container. Otherwise, information technology can coalesce into a large, solid mass. Ammonium nitrate can absorb enough moisture to liquefy. Blending ammonium nitrate with certain other fertilizers can lower the critical relative humidity.[thirty]
The potential for apply of the textile as an explosive has prompted regulatory measures. For case, in Australia, the Dangerous Appurtenances Regulations came into issue in August 2005 to enforce licensing in dealing with such substances.[31] Licenses are granted simply to applicants (manufacture) with appropriate security measures in place to forestall whatsoever misuse.[32] Boosted uses such as didactics and research purposes may also be considered, simply individual use will not. Employees of those with licenses to deal with the substance are yet required to be supervised by authorized personnel and are required to laissez passer a security and national police force check before a license may be granted.
Health hazards [edit]
Ammonium nitrate is not hazardous to wellness and is usually used in fertilizer products.[33] [34] [35]
Ammonium nitrate has an LDl of 2217 mg/kg,[36] which for comparison is virtually two-thirds that of table common salt.
Disasters [edit]
Ammonium nitrate decomposes, non-explosively, into the gases nitrous oxide and water vapor when heated. However, it tin exist induced to decompose explosively past detonation.[37] Large stockpiles of the material can too be a major fire risk due to their supporting oxidation, a situation which can hands escalate to detonation. Explosions are non uncommon: relatively minor incidents occur about years, and several large and devastating explosions have as well occurred. Examples include the Oppau explosion of 1921 (one of the largest bogus non-nuclear explosions), the Texas Metropolis disaster of 1947, the 2015 Tianjin explosions in China, and the 2020 Beirut explosion.[38]
Ammonium nitrate can explode through two mechanisms:
- Daze-to-detonation transition. An explosive charge within or in contact with a mass of ammonium nitrate causes the ammonium nitrate to detonate. Examples of such disasters are Kriewald, Morgan (present-day Sayreville, New Jersey), Oppau, and Tessenderlo.
- Deflagration to detonation transition. The ammonium nitrate explosion results from a fire that spreads into the ammonium nitrate (Texas Urban center, TX; Brest; West, TX; Tianjin; Beirut), or from ammonium nitrate mixing with a combustible material during the fire (Gibbstown, Cherokee, Nadadores). The fire must be confined at least to a caste for successful transition from a fire to an explosion.
See also [edit]
- Resource recovery
References [edit]
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-eight
- ^ Martel, B.; Cassidy, K. (2004). Chemical Risk Assay: A Practical Handbook. Butterworth–Heinemann. p. 362. ISBN1-903996-65-1.
- ^ "Adventure Rating Information for NFPA Fire Diamonds". Archived from the original on 17 February 2015. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ Karl-Heinz Zapp "Ammonium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemical science 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:x.1002/14356007.a02_243
- ^ "Ammonium nitrate production by state, 2019 - knoema.com". Knoema . Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- ^ a b Ammonium nitrate sold by ton as U.S. regulation is stymied. Archived 28 February 2018 at the Wayback Machine – The Dallas Morn News
- ^ "Gwihabaite". www.mindat.org.
- ^ "Niter". world wide web.mindat.org.
- ^ "List of Minerals". www.ima-mineralogy.org. 21 March 2011.
- ^ US 4927617, Villard, Alexandre & Cotonea, Yves, "Process of producing concentrated solutions of ammonium nitrate", published 1990-05-22, assigned to Societe Chimique des Charbonnages South.A.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 469. ISBN978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b "The chemical science behind the Beirut explosion".
- ^ Choi, C. Southward.; Prask, H. J. (1983). "The construction of ND4NOiii phase Five by neutron powder diffraction". Acta Crystallographica B. 39 (4): 414–420. doi:10.1107/S0108768183002669.
- ^ Kumar, Pratim (Dec 2019). "Advances in stage stabilization techniques of AN using KDN and other chemic compounds for preparing light-green oxidizers". Defence force Technology. xv (6): 949–957. doi:10.1016/j.dt.2019.03.002.
- ^ "Nutrient Content of Fertilizer Materials" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2012. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- ^ a b Cook, Melvin A. (1974). The Scientific discipline of Industrial Explosives. IRECO Chemicals. p. one. ASIN B0000EGDJT.
- ^ Brook, Tom Vanden. "Afghan bomb makers shifting to new explosives for IEDs". USA TODAY.
- ^ Coxworth, Ben (20 September 2021). "Sunlight and salt water join forces in electricity-free cooling system". New Atlas. Gizmag Pty Ltd. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ^ United states 5531941, Poole, Donald R., "Process for preparing azide-free gas generant composition", published 1996-07-02, assigned to Automotive Systems Laboratory
- ^ Airbag Chemical compound Has Vexed Takata for Years – The New York Times
- ^ A Cheaper Airbag, and Takata'southward Route to a Deadly Crisis. – The New York Times
- ^ a b c d Chemic Informational: Safe Storage, Handling, and Management of Ammonium Nitrate United States Environmental Protection Bureau
- ^ "Storing and treatment ammonium nitrate" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on four July 2011. Retrieved 22 March 2006.
- ^ "Ammonium nitrate MSDS". Archived from the original on 18 August 2011. Retrieved 25 January 2012.
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik (2002). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Loma. ISBN0-07-049439-8.
- ^ "Ammonium nitrate". PubChem . Retrieved vi August 2020.
- ^ a b "Study for Kooragang Island Update PHA MOD1 Report". Orica Mining Services. 1 April 2012. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ "Chemical Engineering Transactions" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 April 2016.
- ^ "Ammonium Nitrate". webwiser.nlm.nih.gov . Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ Fertilizers Europe (2006). "Guidance for Compatibility of Fertilizer Blending Materials" (PDF).
- ^ "Unsafe Goods (HCDG) Regulations" (PDF).
- ^ Ammonium Nitrate-Regulating its use, Balancing Access & Protection from "Worksafe Victoria". Archived from the original on xi March 2011.
- ^ CF Industries. "Ammonium nitrate MSDS" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2014.
- ^ "Chemicalland21 – Ammonium Nitrate". Archived from the original on 10 January 2012.
- ^ "Ammonium Nitrate". Paton Fertilizers Pty Ltd. 2005.
- ^ "Cloth Safety Data Sheet, Ammonium nitrate MSDS". Archived from the original on 18 August 2011. Retrieved 25 January 2012.
- ^ Chaturvedi, Shalini; Dave, Pragnesh North. (Jan 2013). "Review on Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Nitrate". Journal of Energetic Materials. 31 (ane): 1–26. Bibcode:2013JEnM...31....1C. doi:ten.1080/07370652.2011.573523. S2CID 94427830.
- ^ "Lebanon's president calls for ii-calendar week state of emergency in Beirut after nail". Reuters. Beirut. 4 Baronial 2020. Retrieved 4 August 2020.
Aoun, in remarks published on the Presidency Twitter account, said it was "unacceptable" that 2,750 tonnes of ammonium nitrate was stored in a warehouse for six years without safety measures and vowed that those responsible would face up the "harshest punishments".
Sources [edit]
- Properties: UNIDO and International Fertilizer Evolution Center (1998), Fertilizer Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 0-7923-5032-4.
External links [edit]
- International Chemical Safety Card 0216
- "Storing and Handling Ammonium Nitrate", United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland Health and Safe Executive publication INDG230 (1986)
- Chemical Advisory: Safe Storage, Treatment, and Direction of Ammonium Nitrate The states Ecology Protection Agency
- Calculators: surface tensions, and densities, molarities and molalities of aqueous ammonium nitrate
Ammonium Nitrate Heat Of Formation,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ammonium_nitrate
Posted by: lyonharay1986.blogspot.com



0 Response to "Ammonium Nitrate Heat Of Formation"
Post a Comment